AR Envelope Follower
Overview
AR Envelope Follower, where "AR" stands for Attack-Release, is similar to the Peak Envelope Follower but allows you to specify the attack duration. During the attack phase of an audio signal, the AR envelope follower attempts to follow the signal but is constrained by the attack duration. A longer attack period gives a softer response, exponentially increasing. When the signal level drops below the peak, the follower gradually releases the peak level with an exponential decay.
The AR envelope follower models the behavior of two resistors, one for attack, and one for release, each connected in series with an ideal diode —with no voltage drop—, tied together and connected to a capacitor. During attacks, the capacitor charges through the attack resistor, exponentially increasing. The capacitor discharges through the release resistor as the audio signal falls below the peak charge, causing the output voltage to progressively decay with an exponential curve.
Response
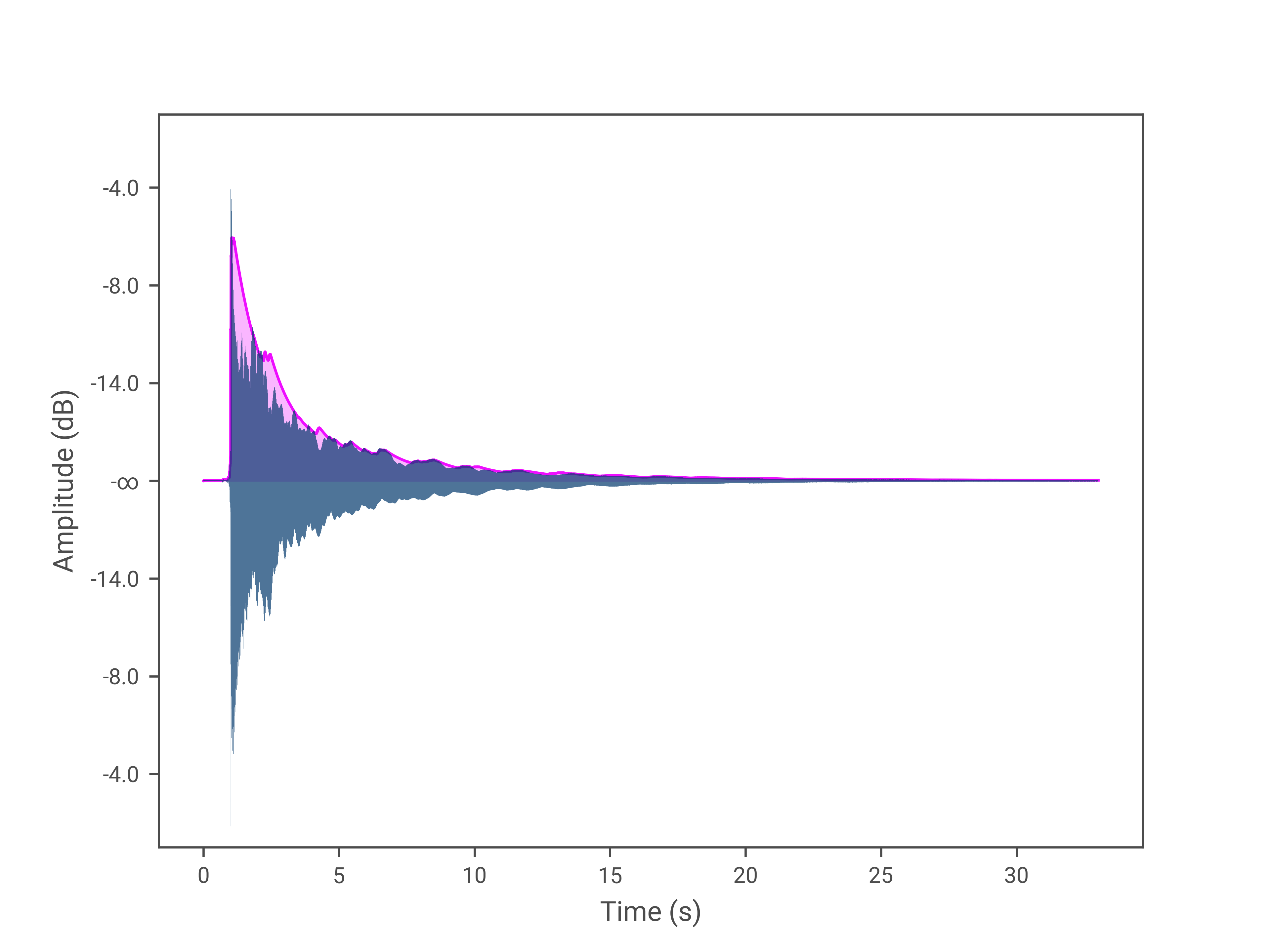
The plot in Figure 1 depicts the response of the AR envelope follower, which was obtained by picking the guitar’s low-E string and using a 2-milliseconds attack duration and 2-second release duration (envelope: magenta, signal: blue, absolute value of the signal: dark blue).
It is worth noting that we use the absolute value of the signal to capture both the positive and negative sides of the waveform, as indicated by the dark blue plot. The AR envelope follower does not perform this operation automatically, allowing you to perform any necessary preprocessing before computing the envelope. This flexibility enables you, for example, to capture only the positive or negative peaks, or perhaps the square of the signal, depending on your application needs.
Like the Peak Envelope Follower, the AR Peak Detector is susceptible to having ripples in the envelope with the short release durations. See Envelope Ripples for details.
Declaration
struct ar_envelope_follower
{
ar_envelope_follower(
duration attack
, duration release
, float sps
);
float operator()(float s);
float operator()() const;
ar_envelope_follower& operator=(float y);
void config(duration attack, duration release, float sps);
void attack(float attack_, float sps);
void release(float release_, float sps);
};Expressions
Notation
env,a,b-
Objects of type
ar_envelope_follower atk,rel-
Objects of type
duration sps-
Floating point value for samples per second.
s-
Floating point value for the latest input sample.
y-
Floating point value from 0.0 to 1.0.
Constructors and Assignment
| Expression | Semantics |
|---|---|
|
Construct a |
|
Copy construct from |
|
Assign |
|
Reset the latest held value of the |
| C++ brace initialization may also be used. |
Function Call
| Expression | Semantics | Return Type |
|---|---|---|
|
Process the input sample |
|
|
Get the latest held value of the
|
|
Mutators
| Expression | Semantics | Return Type |
|---|---|---|
|
Set the attack duration given
|
|
|
Set the attack duration given
|
|
|
Set the release duration given
|
|